The Significance of External Rotation in Abduction in Chiropractic Care
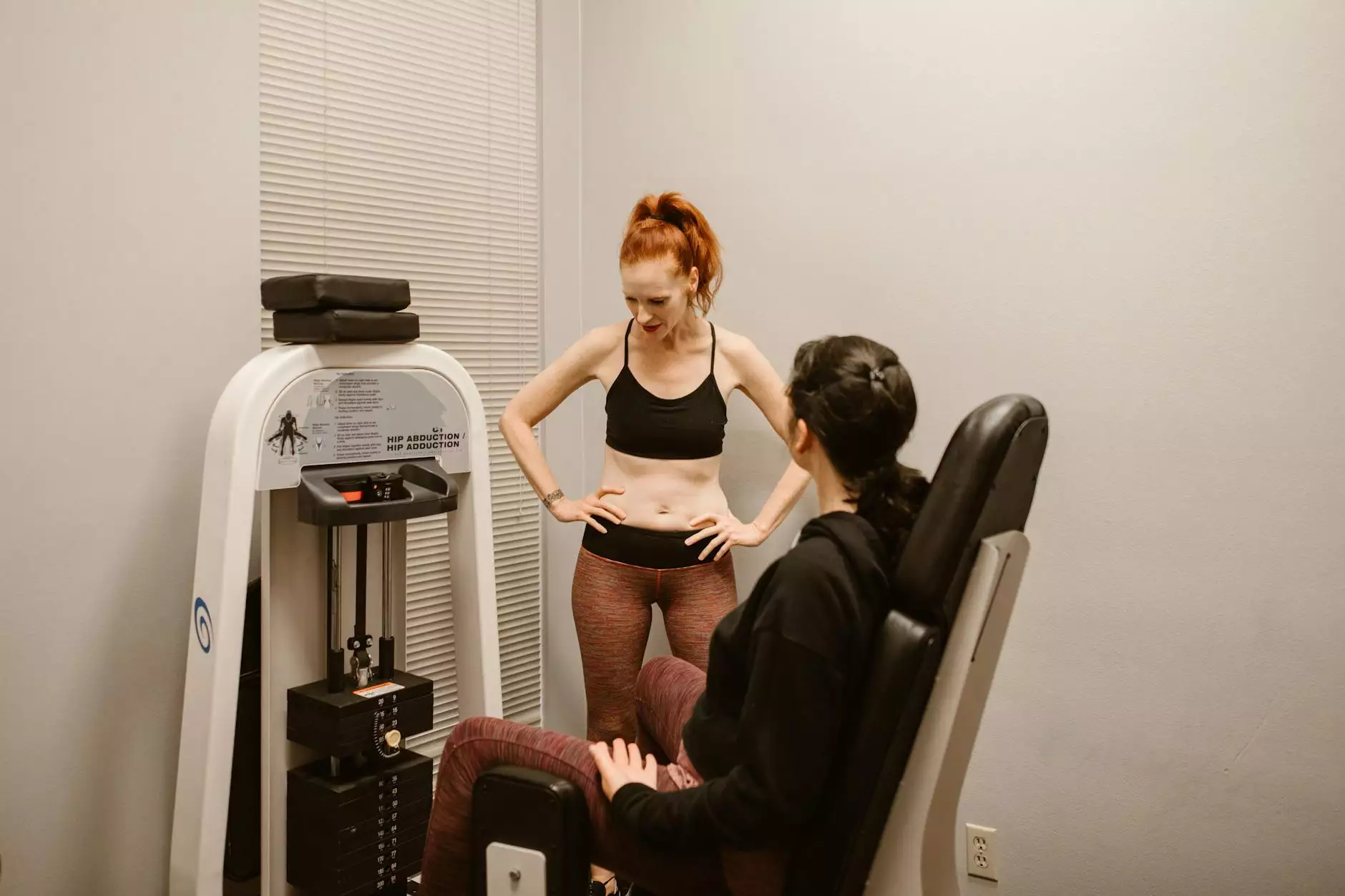

External rotation in abduction is a crucial concept in the fields of anatomy, rehabilitation, and chiropractic care. Understanding this mechanism is vital for health professionals as it plays a pivotal role in patient assessment and treatment strategies. In this article, we will delve deeply into the physiological aspects of this term, its implications in various therapeutic practices, and how it can enhance overall patient well-being.
1. Defining External Rotation and Abduction
To grasp the concept of external rotation in abduction, we must first define the individual components:
- External Rotation: This movement occurs when a limb or body part rotates away from the body's midline. In simpler terms, think of your arm moving outward and away from your chest.
- Abduction: This term refers to the movement of a body part away from the midline of the body. For example, lifting your arms straight out to the side is a classic example of abduction.
When combined, external rotation in abduction describes a specific motion where a limb moves away from the center of the body while simultaneously rotating outward. This complex movement is essential in various physical activities, including sports, daily tasks, and therapeutic exercises.
2. The Role of External Rotation in Abduction in Daily Movement
Understanding the mechanics of external rotation in abduction is vital for recognizing how it affects daily movements.
Every time we reach for an object, wave, or engage in physical activities like swimming or throwing, our body utilizes this movement pattern. It is particularly noticeable in the shoulder joint and the hip joint:
- Shoulder Joint: In actions like throwing a ball, the arm must abduct and externally rotate to achieve maximum range and power.
- Hip Joint: When performing exercises such as lateral lunges or leg raises, the hip must also coordinate abduction with external rotation to maintain balance and stability.
A clear understanding of this movement is essential for coaches, trainers, and therapists to optimize performance and prevent injuries.
3. Clinical Relevance of External Rotation in Abduction
In the clinical setting, the understanding of external rotation in abduction becomes even more critical. It provides insights into diagnosis, rehabilitation, and treatment:
3.1. Diagnosis of Injuries
Injuries to the rotator cuff, for example, often involve compromised external rotation capabilities. Physical therapists assess the degree of external rotation in abduction as part of a comprehensive shoulder examination. If a patient presents with limited range of motion in this area, it may indicate specific injuries or pathologies.
3.2. Rehabilitation Protocols
Rehabilitation programs often incorporate exercises that facilitate the recovery of external rotation in abduction. Effective rehabilitation might include:
- Isometric external rotation exercises
- Resistance training with bands or weights to improve muscular strength
- Stretching routines focusing on the shoulder or hip to regain flexibility
Incorporating these specific movements helps to restore functionality and prevent complications.
4. Impacts on Sport Performance
Athletes, particularly those participating in sports requiring rapid limb movements, heavily rely on the mechanics of external rotation in abduction. From baseball pitchers to tennis players, performing these motions optimally can enhance performance and reduce injury risk.
4.1. Improving Throwing Mechanics
In baseball, for instance, a pitcher's ability to effectively rotate their arm in the external abduction position can add velocity and accuracy to their throws. Strengthening the muscles responsible for this movement is vital for long-term athletic success.
4.2. Enhancing Overall Athletic Capability
In many sports such as gymnastics, swimming, and martial arts, mastering abduction with external rotation enables athletes to perform complex movements with greater ease and efficacy.
5. Education and Training for Health Professionals
The role of health and medical professionals in educating others about external rotation in abduction cannot be understated. Knowledge dissemination is essential in ensuring proper execution of movement and understanding the implications on health.
5.1. Continuing Education Programs
Institutions such as IAOM-US offer continuing education programs focusing on functional movements, which include comprehensive training on external rotation in abduction. By attending these courses, professionals can stay updated on the latest techniques and research in rehabilitation and performance.
5.2. Integrating Knowledge into Practice
Practitioners who incorporate this understanding into their practice can create more personalized and effective treatment plans for their patients. This knowledge allows therapists to better educate patients on their own movements and the importance of correct biomechanics.
6. Concluding Thoughts
In conclusion, external rotation in abduction is not just a technical term but a vital movement that significantly influences health, performance, and function in daily life. For health and medical professionals, understanding this movement is key to diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal conditions effectively.
Continued education in this area is essential, as high-quality training not only enhances professional skill sets but also leads to better patient outcomes. With greater awareness and understanding of external rotation in abduction, clinicians can promote optimal functional movement patterns that lead to healthier, more active lives.
7. Further Resources
For additional information, consider exploring the following resources:
- IAOM-US Official Website: A plethora of educational resources catering to healthcare professionals.
- Latest Research Articles: Journal publications on biomechanics and rehabilitation.
- Online Courses: Enroll in workshops focused on advanced physical therapy and chiropractic methods.